Scroll to:
Digital Model of the Turgoyak Lake System, Southern Urals
https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2025.2.20
Abstract
The sediments of Lake Turgoyak (Southern Urals, Russia) have been accumulating throughout the Late Pleistocene and the Holocene. Sedimentation is controlled by the lake’s morphometry, drainage systems, vertical zoning, thermal state of the water, and wind action.
Therefore, analysis of cartographic materials illustrating the area’s geology, topography, drainage systems, watersheds (catchment areas) and drainage divides is relevant in this regard. All these aspects are important for assessing the role of sediment sources and transportation routes, as well as deposition mechanisms and sediment distribution within the lake. The study of lake deposits provides valuable insights for genetic interpretation of sedimentary sequences in the context of paleoclimatic and paleoecological trends and events.
This study presents a digital model of Lake Turgoyak and its surroundings. The model was developed using GIS software, incorporating available geological, topographical, and bathymetric maps. Overlaying watershed models onto geological maps of pre-Quaternary and Quaternary deposits enabled assumptions about the material composition of sediment transported into the lake.
Developing similar digital models for lake systems in the Urals, other regions of Russia, and worldwide opens opportunities to systematize information at a new level and utilize it for various reconstructive purposes.
Keywords
For citations:
Chernova I.Yu., Kosareva L.R., Nourgalieva N.G., Chernova O.S. Digital Model of the Turgoyak Lake System, Southern Urals. Georesursy = Georesources. 2025;27(2):264–280. https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2025.2.20
Introduction
Lake Turgoyak is a unique natural feature and one of the largest sources of drinking water in the Southern Urals. It is rightfully called the “younger brother of Baikal” for the purity and clarity of its water. The lake has held the status of a regional natural monument since 1961. It is also worth noting that Lake Turgoyak is one of the most thoroughly studied lakes in the Southern Urals across various aspects: hydrography, ecology, geology, and climatology (Andreeva, 1973; Rogozin, Takachev 1998; Gavrilkina et al., 1998; Diyanova, Deryagin 2010; Zakharov, 2020, 2021; Kostryukova et al., 2022; Maslennikova et al., 2018; Kosareva et al, 2023, and others).
The sediments of Lake Turgoyak have been accumulating throughout the Late Pleistocene and the Holocene; the lake is at least 25,000 years old (Maslennikova et al., 2018; Kosareva et al., 2023). The lithogenetic features of the lake sediments are primarily explained by the initial stages of lithogenesis: erosion and deposition in conditions of high sensitivity of the lake system to climatic changes. These changes affect the intensity of sedimentary material mobilization in the ultimate provenance, on drainage divides and in watersheds, along material transportation routes, and in the deposition area. The distribution of sedimentary material within the lake during sedimentation is controlled by the lake’s morphometry, drainage system arrangement, vertical zoning, thermal state of the water, and wind action.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used worldwide for mapping lake systems with various objectives. Examples include: studying floods caused by outbursts of the glacial lakes Lahul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh, India) (Rongali et al., 2024); mapping and monitoring thermokarst lakes to evaluate climate change impact on permafrost regions and quantify carbon dioxide emissions (lakes located in the Beiluhe basin on the central Tibetan Plateau and in northern Seward Peninsula, western Alaska) (Qin et al., 2023); investigating morphometric changes in Lake Hawassa (Ethiopian Rift Valley), which is vital for the local population (Menberu et al., 2021); researching Lake Burullus (north of the Nile Delta, Egypt), highlighting the importance of mapping for environmental studies and surface water pollution analysis, under the circumstances of the growing water demand due to intensive agriculture and economic growth (Masoud et al., 2021).
In Russia, GIS has been used to determine morphometric characteristics of lake basins located in the Nizhny Novgorod region and create digital models of the said basins (Artaev, Bayanov, 2015; Astashin et al., 2016). For geological and ecological monitoring of Lake Baikal, information services have been created, providing open access to monitoring results and cartographic resources (BaikalGIS.com 2024).
A digital bathymetric model of Lake Onega was developed to enable modeling of past basin relief changes and three-dimensional modeling of modern processes, as well as to refine the primary morphometric characteristics of the lake and its various zones (Potakhin et al., 2024).
Therefore, analysis of cartographic materials illustrating the area’s geology, topography, drainage systems, watersheds and drainage divides is relevant in this regard. All these aspects are important for assessing the role of sediment sources and transportation routes, as well as deposition mechanisms and sediment distribution within the lake. It should be noted that identification of sources and pathways of pollutants entering the lake is also one of the pressing issues.
Geographic Information Systems provide specialized tools for identifying spatial patterns within a set of specified objects. Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) are valuable sources of elevation data, representing the study area as a regular grid, which enables a wide range of morphometric analysis methods to be applied in the study, including slope and runoff mapping, modeling of drainage systems and watersheds, and more.
The aim of this project is to create a digital model of the Turgoyak lake system (based on existing cartographic materials), which includes geological structure of the area, topography, maximum water level, bathymetry, watersheds, drainage divides, and drainage systems.
Study area
Turgoyak is an oligotrophic, open lake located in a narrow intermountain basin, squeezed between the Ural Tau and Ilmensky ranges (Fig. 1c). The lake’s watershed is quite limited, since it is defined not by large mountains, but by relatively low ridges and chains of individual hills surrounding the lake from all directions. The Zaozernyi ridge semicircularly confines the watershed from the west and partially from the south and north. Chains of low peaks and hills also form a semicircle limiting the watershed from the east, north, and south (Fig. 1d).
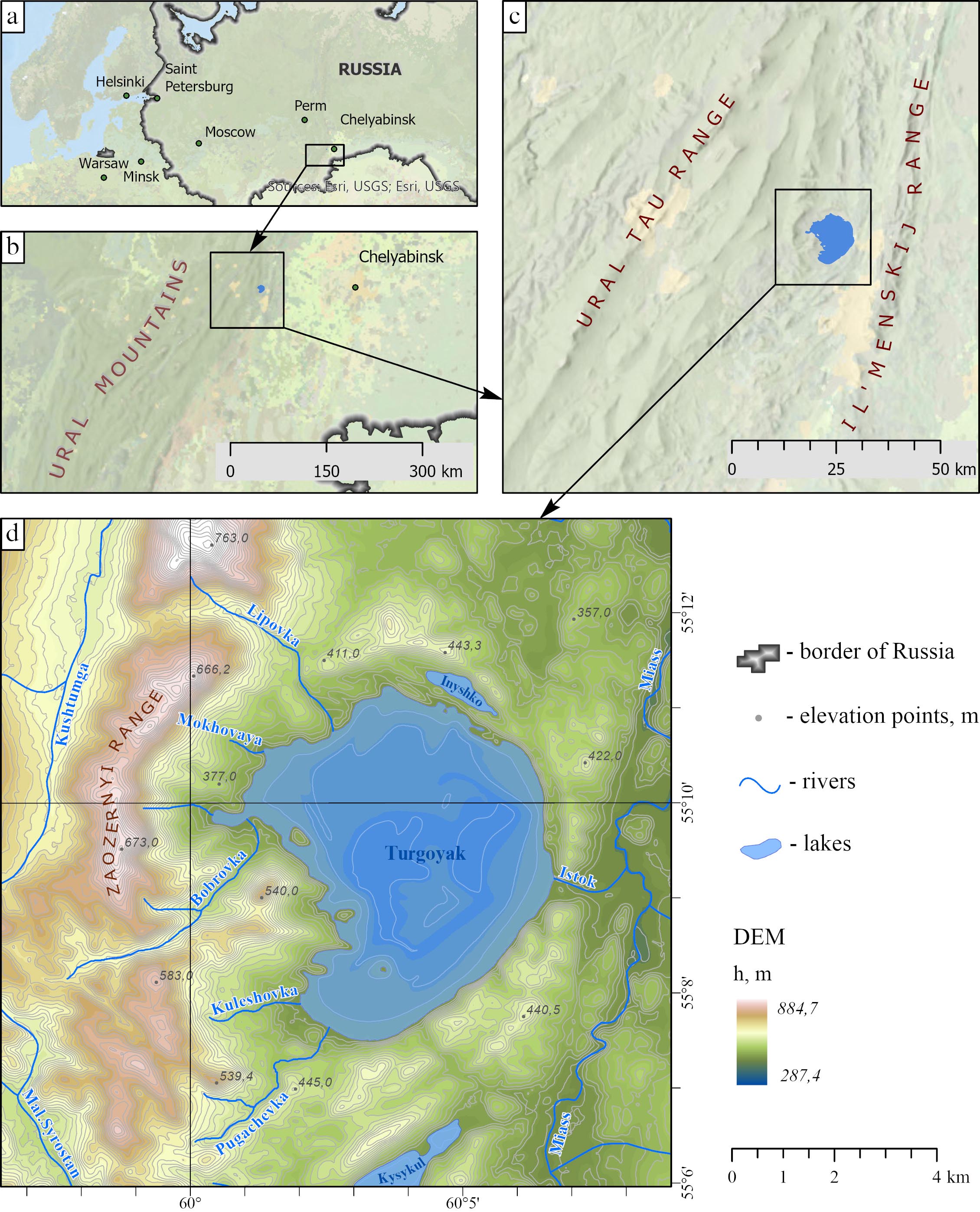
Fig. 1. Overview map: a) study area on the map of Russia; b) Southern Urals region; c) location of Lake Turgoyak in an intermountain basin; d) topography and hydrography of the study area
The main morphometric parameters of the lake are as follows: the elevation above sea level is 320 m, the water surface area is 26.4 km², the average depth is 19.2 m (Andreeva, 1973; Zakharov, 2020), and the maximum depth is 32.5 m (Zakharov, 2020) (according to other data, it reaches 34 m (Andreeva, 1973)). Turgoyak has the greatest average depth of all tectonic lakes in the Southern Urals.
The lake’s shoreline is close to circular in the eastern part, but heavily indented with capes and bays in the western part. The western and eastern shores are high (up to 50–100 m) and often steep (Zakharov, 2020). According to seismoacoustic studies (Kosareva et al., 2023), the bottom of the lake is uneven, cut by underwater ridges and bald peaks, the largest of which rise above the water surface as islands. Turgoyak has 6 islands, the largest being Vera, known for its megalithic complex (Grigoriev, Vasina, 2019).
Vera Island is a historical, cultural, and natural ecosystem, recognized as a regional cultural heritage site. It hosts 38 archaeological monuments spanning different eras. The oldest date back to the Paleolithic (100,000–40,000 years ago), while the most recent – the ruins of an Old Believers’ hermitage – belongs to the 19th century. The most prominent period represented on the island is the Chalcolithic (4th–3rd millennium BCE), evidenced by three chambered megaliths and ritual sites (Grigoriev, Vasina, 2019, 2020).
The lake basin is of tectonic origin, and is located within the Turgoyakskiy granitoid Massif, which is a circular stock. A significant part of it is hidden beneath the lake waters (Petrov et al., 2015; Snachev et al., 2020; Fershtater et al., 2000). The Turgoyakskiy Massif belongs to the Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy complex (γδС1–2ts) of the monzodiorite-granite formation. The intrusive complex is composed predominantly of granodiorite, less commonly of quartz diorite and intrusive granite. The Massif has intrusive contacts with the host rocks, which is expressed in their hornfelsing, i.e. transformation into fine-grained amphibole hornfelses (Snachev et al., 2020; Fershtater et al., 2000).
Amphibole-biotite granodiorites are predominantly gneissic, often porphyritic rocks consisting of plagioclase, potassium feldspar (microcline-perthite), quartz, biotite, amphibole (hornblende), and accessory minerals (sphene, apatite, epidote, garnet, zircon, pyrite, magnetite). The granites are composed of biotite, less commonly amphibole-biotite varieties, which include: oligoclase, microcline or orthoclase, quartz, biotite, hornblende, and accessory minerals – sphene, epidote, apatite, garnet, pyrite. The rocks of the Turgoyakskiy intrusive complex are characterized by elevated alkali content (Shagalov, 2000; Snachev et al., 2020; Petrov et al., 2015).
Turgoyak’s hydrographic network is represented by rivers and streams: Lipovka, Bobrovka, Kuleshovka, Pugachyovka, Mokhovaya, Ugolny, and Krutaya (Zakharov, 2018). These are relatively small streams flowing down from the surrounding ridges. Additionally, the “Turgoyak-2021” expedition identified three more permanent streams (Mishutkina et al., 2021). Only one small river, Istok, flows out of the southeastern part of the lake, connecting it with the Miass river (Fig. 1d).
Due to the small size of the watershed area, surface runoff plays a minor role in the lake’s water supply. Groundwater plays the main role in feeding the lake. Lake Inyshko, which has an indistinct connection with Turgoyak, is also located within the watershed. The lakes are separated by a narrow 200-meter land neck. There’s a known hydraulic connection between the lakes (Special Protection Natural Areas of Russia 2024), but water overflows across the land neck are also possible.
When calculating the watershed model, Lake Inyshko’s watershed was considered part of Lake Turgoyak’s watershed.
Materials and methods
To create the most comprehensive digital model of the lake system, the GIS project incorporated layers from the digital State Geological Map of the Russian Federation (scale 1:200,000), specifically sheets N-41-VII and N-40-XII (Petrov et al., 2003; Aulov et al., 2015). The geological maps were provided by VSEGEI (A.P. Karpinsky Russian Geological Research Institute, 2024) upon request. The model utilized both pre-Quaternary and Quaternary deposit maps.
The geological layers were clipped to the study area’s boundary. At the junction of adjacent sheets, the boundaries of geological polygons were adjusted (through edge matching), and the attributes of the polygons were checked and corrected. This resulted in a seamless digital geological map of pre-Quaternary (Fig. 2) and Quaternary (Fig. 3) deposits within the study area.
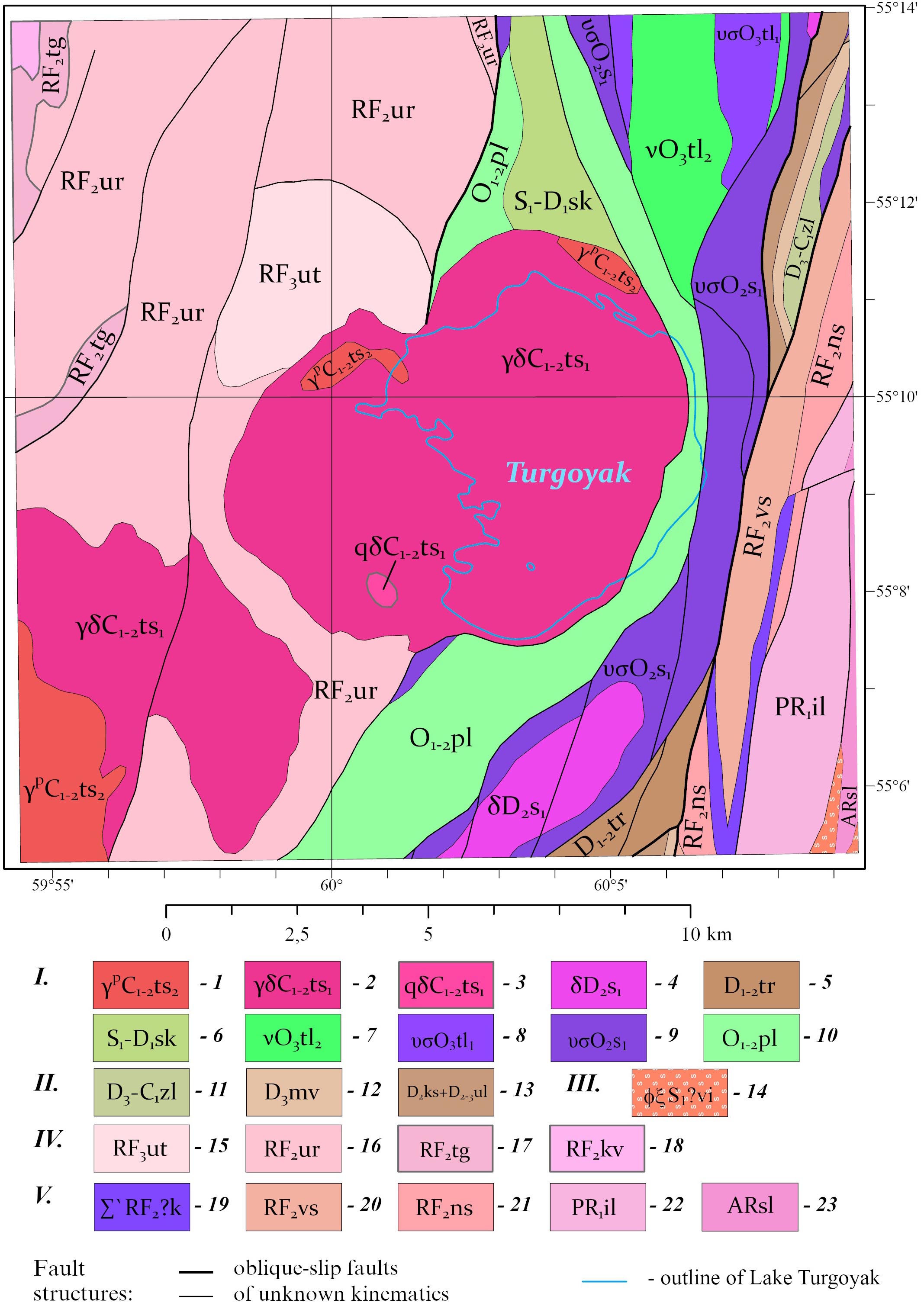
Fig. 2. Digital geological map of pre-Quaternary deposits in the study area, compiled based on the State Geological Map of the Russian Federation at a scale of 1:200,000, sheets N-41-VII and N-40-XII (Petrov et al. 2003; Aulov et al. 2015).
Legend: I. Voznesensko-Prisakmarskaya structural zone: 1 – Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy diorite-granodiorite-granite complex. Second phase: two-feldspar granite with predominant plagioclase; granite dikes, moderately alkaline granite dikes (εγ), granite-porphyry dikes, aplite dikes. 2 – Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy diorite-granodiorite-granite complex. First phase: granodiorite, quartz diorite (qδ); granodiorite dikes; granodiorite-porphyry dikes. 3 – Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy diorite-granodiorite-granite complex. First phase: quartz diorite (qδ). 4 – Salavatskiy diorite-plagiogranite complex. First phase: diorite, quartz diorite; diorite dikes; propylite. 5 – Turatskaya Suite. Polymictic conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, marbleized limestone, marble (300–500 m). 6 – Sakmarskaya Suite. Carbonaceous-siliceous and carbonaceous-clay schist (400–500 m). 7 – Talovsky dunite-wehrlite-clinopyroxenite-gabbro complex. Second phase: gabbro. 8 – Talovsky dunite-wehrlite-clinopyroxenite-gabbro complex. First phase: clinopyroxenite, wehrlite; serpentinized dunite (σ). 9 – Sakmarskiy gabbro-dunite-harzburgite complex. First phase: serpentinized dunite, harzburgite; talc-carbonate, talc rocks; listvenite (l). 10 – Polyakovskaya Suite. Sodium metabasalt (aphyric, rarely porphyritic), chlorite-siliceous schist, quartzite, siliceous metatuffite, volcanomictic metasandstone (800–1000 m). II. Zapadnomagnitogorskaya structural zone: 11 – Zilairskaya Suite. Polymictic conglomerate, gravelite, sandstone, siltstone, siliceous-clay schist (500 m). 12 – Mukasovskaya Suite. Siliceous schist, siliceous-clay schist, siliceous tuffite, tuff siltstone (100 m). 13 – Combined Karamalytashskaya and Ulutauskaya Suites. Amphibole basalt, fine-porphyry basalt, hyalobasalt and hyaloclastite, basaltic andesite, andesite, dacite, plagioryodacite, plagioryolite, plagioryolite tuff, tuffite, tuff sandstone, tuff siltstone, siliceous-clay and siliceous schist, jasper and limestone. Polymictic conglomerate, volcanomictic sandstone, siltstone, siliceous schist in the upper part (1800 m). III. Sysertsko-Ilmenogorskaya structural zone: 14 – Vishnevogorsko-Ilmenogorskiy carbonatite-miaskite complex. Biotite miaskite, biotite-amphibole miaskite, biotite syenite, amphibole syenite, corundum syenite, nepheline-feldspar pegmatite, carbonatite, pyroxene syenite (Еξ), fenite, biotite-feldspar, pyroxene-feldspar and carbonate-silicate rocks. IV. Central Ural megazone, Zlatoustovskaya structural zone: 15 – Uytashskaya Suite. Micaceous metasandstone, mica-quartz schist, quartzite sandstone, quartz-muscovite schist, interlayers of “ore” sandstones with hematite, ilmenite, magnetite, zircon (300 m). 16 – Urenginskaya Suite. Crystalline schist with garnet, staurolite, graphite, chloritoid, micaceous quartzite and marble (2000 m). 17 – Taganayskaya Suite. Quartzite, often aventurine, quartzite-like sandstone, phyllite-like schist with chloritoid and graphite, two-mica garnet-staurolite-sillimanite-bearing schist, conglomerate (200–500 m). 18 – Kuvashskaya Suite. Metatrachyrhyolite, metarhyolite, metatrachyrhyodacite, less commonly trachyrhyolite, rhyolite, trachyrhyodacite, two-mica quartz and feldspar-quartz crystalline schist, feldspar-epidote-garnet-bearing schist, amphibolite, amphibolite schist, metabasalt, quartz-feldspar-actinolite-chlorite schist, quartz-feldspar-epidote-chlorite schist, quartz-feldspar-epidote-hornblende schist, phyllite-like graphite-chloritoid-bearing schist, garnet-staurolite-kyanite-sillimanite-bearing schist, acidic metatuff and metatuff breccia, quartzite, conglomerate, dolomitic marble, quartzite sandstone (over 3500 m). V – East Ural megazone, Ilmenogorskaya structural zone: 19 – Kaganskiy complex of metamorphosed ultramafic rocks and gabbroids. Antigorite serpentinite, olivine-antigorite, olivine-talc, enstatite-talc-anthophyllite, tremolite rocks, rare clinopyroxenite and gabbroids, talcites. 20 – Verkhnesaitovskaya Suite. Amphibole plagioclase schist, garnet-biotite-amphibole, amphibole-biotite, biotite and garnet-biotite schist, interlayers of graphitic, phosphorite-bearing quartzite (560 m). 21 – Nizhnesaitovskaya Suite. Amphibole plagioclase schist, interlayers of biotite and garnet-biotite plagioclase schist and quartzite (760 m). 22 – Ilmenogorskaya sequence. Amphibolite, sometimes with biotite, garnet, pyroxene; biotite plagiogneiss, amphibole-biotite, garnet-biotite with sillimanite, garnet-biotite quartzite, graphitic quartzite, pyroxene-plagioclase crystalline schist (600–1100 m). 23 – Selyankinskaya Suite. Biotite plagiogneiss, garnet-biotite plagiogneiss, sometimes with sillimanite and graphite, amphibolite with garnet, clinopyroxene, less commonly diopside-plagioclase crystalline schist and quartzite (1000 m). 24 – outline of the current shoreline of Lake Turgoyak.
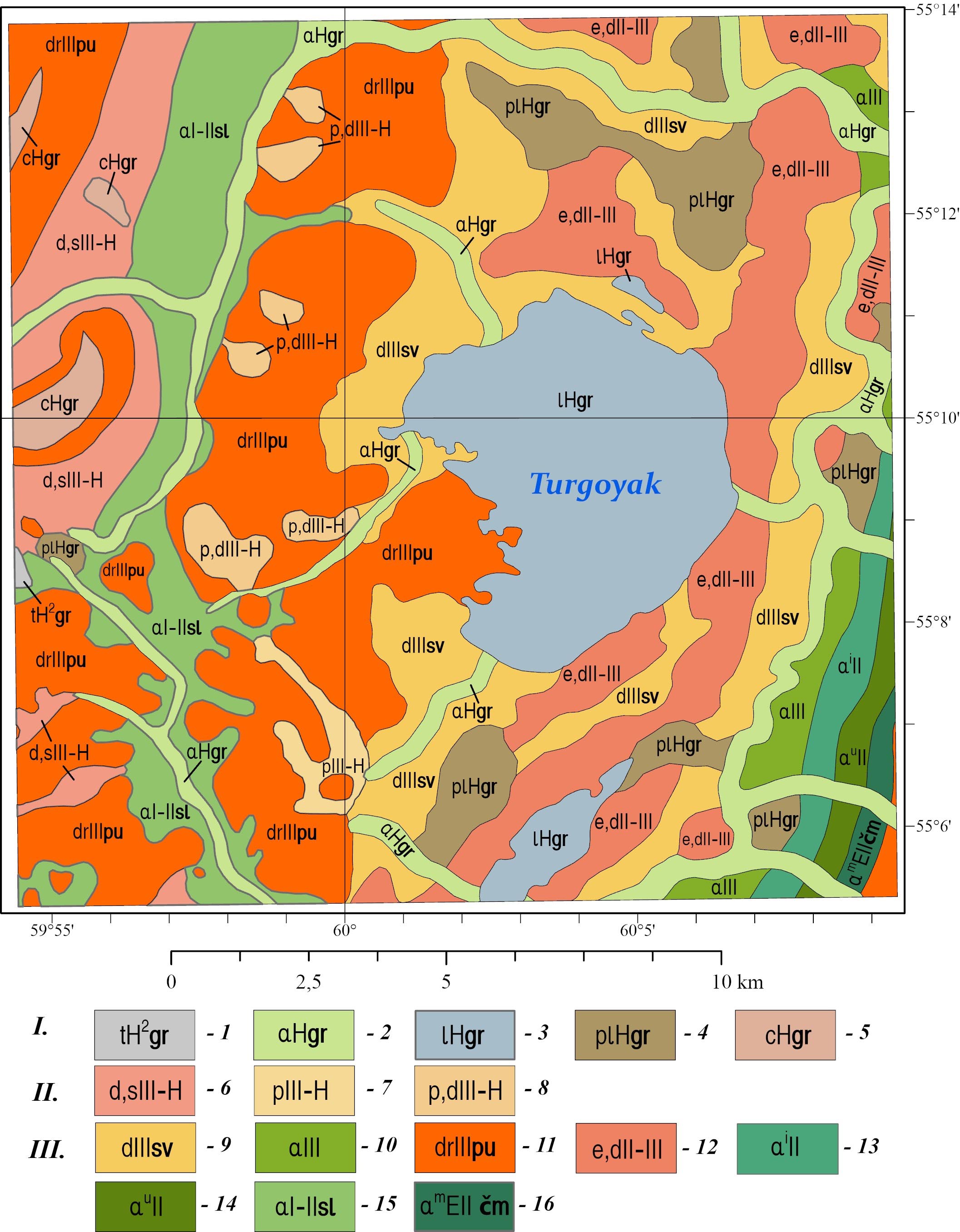
Fig. 3. Digital geological map of Quaternary deposits in the study area, compiled based on the State Geological Map of the Russian Federation at a scale of 1:200,000, sheets N-41-VII and N-40-XII (Petrov et al. 2003; Aulov et al. 2015).
Legend: I – Holocene. 1 – Gorbunovskiy Horizon. Upper Part. Technogenic deposits. Rubble, gruss, clay, gravelly sand, pebble, silt (5–100 m). 2 – Gorbunovskiy Horizon. Alluvial deposits of floodplain terraces and streambeds. Polymictic sand with gravel, silty clay, peaty clay, pebble, boulders (up to 10 m). 3 – Gorbunovskiy Horizon. Lakebed deposits. Sand, silt, silty clay (up to 2 m). 4 – Gorbunovskiy Horizon. Palustrine deposits. Silty clay, peaty clay, peat (up to 8 m). 5 – Gorbunovskiy Horizon. Colluvial deposits. Bouldery debris, rubble, gruss (up to 10 m). II – Upper Neopleistocene–Holocene. 6 – Undifferentiated deluvial and solifluction deposits. Loam, clay, and sandy loam with pebble, gravel, and rubble (>20 m). 7 – Proluvial deposits. Loam and clayey sand with pebble and boulders (5–10 m). 8 – Undifferentiated proluvial and deluvial deposits. Loam and clay with pebble and rubble, gravel beds, sand (4–44 m). III – Pleistocene. 9 – Severouralskiy Superhorizon. Deluvial deposits. Brown loam with gruss, rubble, and sparse local gravel (up to 6 m). 10 – Combined alluvial deposits of Kamyshlovskaya and Rezhevskaya Terraces. Polymictic sand with gravel and pebble, sandy clay, peaty clay, loam, silt, gravel, pebble (up to 18 m). 11 – Polyarnouralskiy Horizon. Deserpation deposits. Boulders, rubble, sandy clay with rubble (up to 15 m). 12 – Eluvial and deluvial deposits. Weathered rubble of bedrock with loamy matrix, gruss, and sparse pebbles (up to 2 m). 13 – Alluvial deposits of Isetskaya Terrace. Loam, polymictic sand with gravel and pebble (up to 15 m). 14 – Alluvial deposits of Ufimskaya Terrace. Loam, polymictic sand, interbeds of gravel with pebble (up to 20 m). 15 – Neopleistocene. Sylvitskiy Horizon, undifferentiated. Alluvial deposits of ancient river valleys. Loam, clay, sand (occasionally with gravel, pebble, and rubble), gravel beds (up to 31 m). 16 – Chumlyakskiy Horizon. Alluvial deposits of Miasskaya Terrace. Polymictic sand with gravel admixture, loam with buried soils, gravel, pebble (up to 20 m). *Thicknesses of Quaternary deposits are given for sheets N-41-VII and N-40-XII, not the study area.
Digital Elevation Model and Hydrological Modeling Tools
The digital elevation model (DEM) shown in Figure 1d was created using all available topographic information sources, and the bathymetry data for Lake Turgoyak (Turgoyak. The lake is a natural monument…, 1993; Zakharov 2018). This DEM encompasses both the land surface and the lake bottom topography.
The Copernicus DEM GLO-30 model, provided by the European Space Agency, served as the primary source for creating the DEM. This model is a digital surface model (DSM) that captures the Earth’s surface, including buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation. It offers a resolution of 1 arc-second (roughly 30 m), with a vertical accuracy of 4 m and a horizontal accuracy of 6 m. To supplement the land elevation data, topographic map sheets at 1:100,000 scale (sheets N40-36 and N41-25) were used. For the lake bottom topography, data from the (Turgoyak. The lake is a natural monument…, 1993) source were taken. Elevation points and lake depth contours were digitized from the topographic sheets and the map taken from the (Turgoyak. The lake is a natural monument…, 1993) source, and then incorporated into the GIS project.
Data preprocessing, hydrological modeling, and map layout creation were carried out in ArcGIS Pro 3.0.2, featuring the Spatial Analyst extension (ESRI ArcGIS Pro 2024).
Since the Copernicus DEM is a surface model rather than a terrain model, several processing and refinement steps were necessary, including removing heights associated with man-made structures, smoothing the surface, and eliminating roughness caused by vegetation, small objects, satellite data processing artifacts, and other factors.
For a smooth DEM suitable for hydrological modeling, the input data underwent several processing steps:
Step 1: The Contour tool was used to extract contours from the DSM. The shape-defining vertices of these contours were then converted to points, retaining their elevation attributes, through the use of the Feature Vertices To Points tool. Subsequently, in editing mode, points associated with roads were removed.
Step 2: The Topo to Raster tool (Spatial Analyst) was used to generate the DEM. The input data for this tool included the points obtained from the previous processing step, elevation points extracted from 1:100,000 scale topographic maps, and contours representing the lake bottom topography. Finally, the Focal Statistics tool (Spatial Analyst) was used to smooth the resulting DEM (with a processing neighborhood of 10x10 cells and Mean as the statistics type).
The Hydrology toolset from the Spatial Analyst extension was employed for hydrological modeling and calculation of watershed surface area (ESRI ArcGIS Pro 2024). The following tools were applied sequentially to the DEM processing:
– FILL was used to eliminate small imperfections in the DEM by filling local depressions in the surface raster that might hinder drainage network extraction. The output is a raster named DEMFill.
– FLOW DIRECTION was applied to the DEMFill raster in order to produce the FlowDirDEM raster, which represents the flow direction from each raster cell.
Then, the FlowDirDEM raster was utilized twice: once for watershed surface area calculation and once for drainage network extraction.
The WATERSHED tool was employed to determine the watershed surface areas.
The extraction of drainage networks and identification of source points involved application of several tools:
– FLOW ACCUMULATION tool computes accumulated flow from the FlowDirDEM raster. The accumulated flow is based on the number of cells, flowing into each receiving downslope cell. Cells with high flow accumulation represent areas of concentrated flow and can be used to identify stream beds. The output of this tool is the FlowAccDEM raster;
– the CON function in Raster Calculator extracts the stream network from the FlowAccDEM raster;
– the STREAMORDER function assigns a numeric order to segments of a raster representing streams, considering both stream lines and steepest descent directions from each raster cell. The Strahler method was used for assigning stream order (Tarboton et al., 1991);
– the STREAM TO FEATURE tool converts the raster stream network to a vector model, preserving the stream order for each linear segment.
According to the Strahler system, a first-order stream has no other streams flowing into it. When two first-order streams join, they form a second-order stream. Stream order only increases when streams of the same order intersect, therefore when two streams with different orders join (for example, first and second), the resulting stream has the same order as the highest order of the two joining streams (second, in the example given). Intersection of two second-order streams creates a third-order stream, and so on.
Under similar physical, geographical and geological conditions, streams of the same order typically share comparable characteristics: length, basin size and flow rate. Therefore, they tend to affect the terrain with similar erosional force. Notably, when same-order streams join, the flow approximately doubles. It then gradually increases downstream due to lateral inflow and contributions from lower-order streams.
Results and discussion
Figure 4 depicts the process of creating a smooth DEM and its final result. Figure 4a and Inset 4d show the original Copernicus DEM. A linear height anomaly associated with a road embankment is clearly visible in this model. The jagged contour lines reflect fine-scale noise. Figure 4b displays the result of removing points related to the road surface. Figures 4c and 3e demonstrate that the road embankment was removed from the elevation surface. Moreover, high-frequency noise was eliminated too, giving the surface a smoother appearance more characteristic of natural terrain.
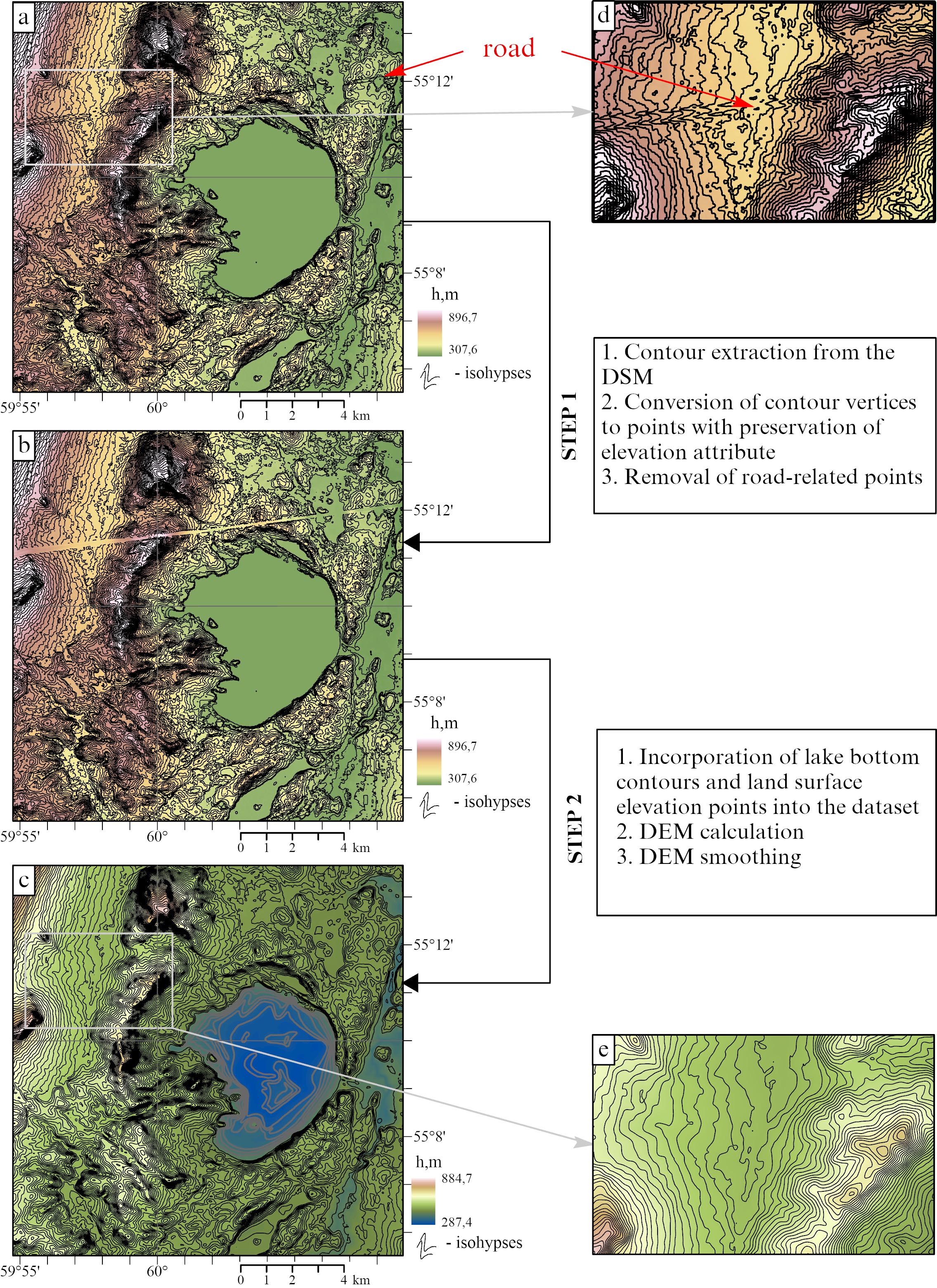
Fig. 4. DEM calculation stages: a) DSM with elevation contours; b) DSM with elevation contours after removal of road-related segments; c) smoothed digital elevation model, including the lake basin topography; d) part of figure a; e) part of figure c. Insets d and e show the same area.
According to the DEM, the maximum elevation in the area is 884.7 m, which aligns with topographic maps when accounting for the Copernicus DEM’s margin of error. The lowest point in the model is located at 287.4 m.
Figure 5 presents the results of hydrological modeling.
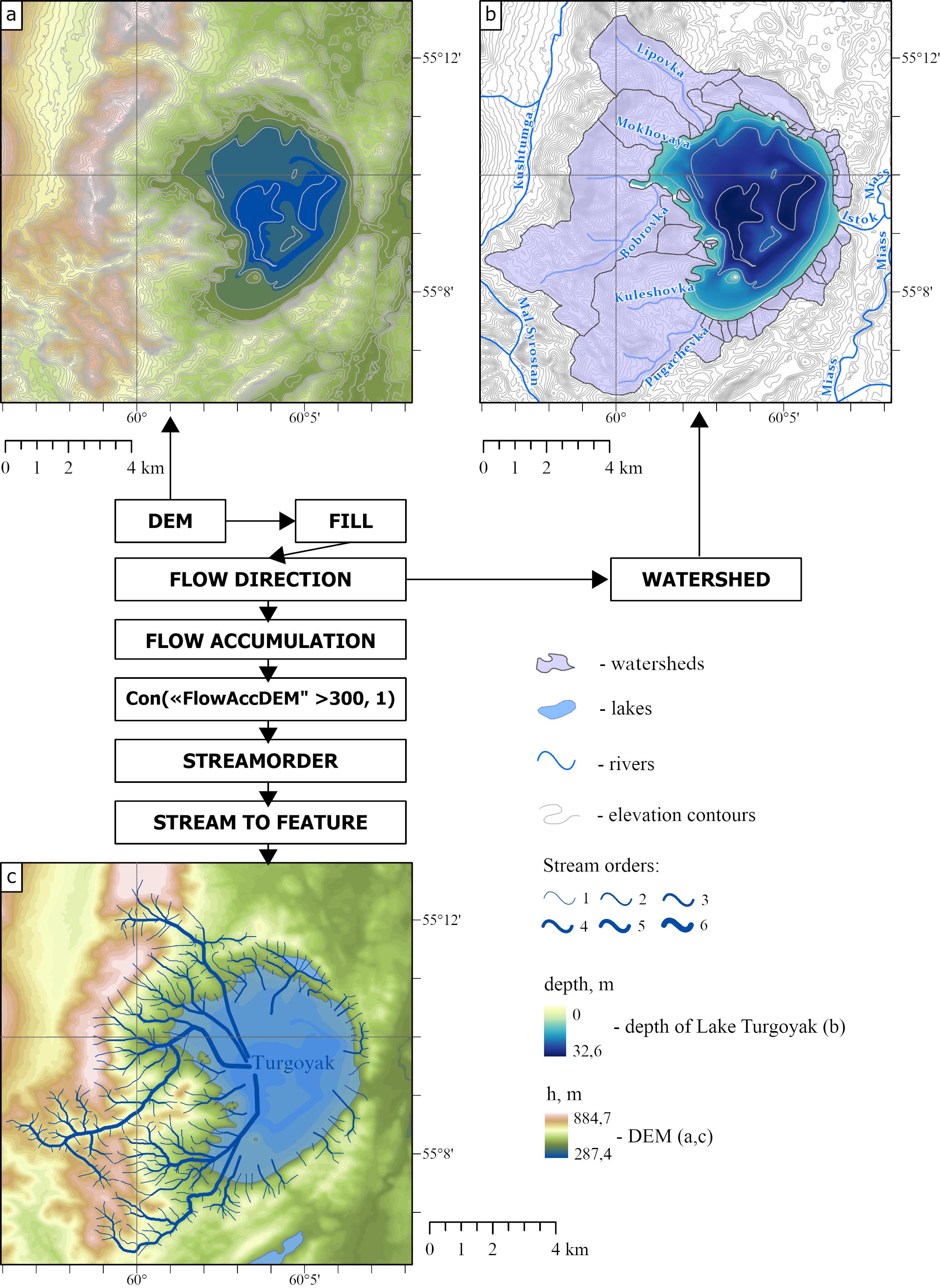
Fig. 5. Hydrological modeling results: a) DEM; b) watersheds; c) drainage networks
The application of FILL and FLOW DIRECTION tools eliminated minor DEM artifacts that would have hindered drainage network extraction (Fig. 5a). Watersheds are shown in Fig. 5b.
Figure 5c displays the final modeling result, obtained through the use of FLOW ACCUMULATION, CON, STREAMORDER, and STREAM TO FEATURE tools.
Figure 6 presents another morphometric parameter – the DEM slope. Slope directly influences the intensity of both linear and sheet erosion, therefore determining the intensity of suspended sediment runoff.

Fig. 6. DEM slope
All other conditions being equal, velocity of flow and changes in its carrying capacity depend on the base level of erosion and slope shape. Erosive forces reach their maximum with steep slopes and a low base level of erosion.
Figures 7 and 8 show the integrated geological/hydrological model of the Turgoyak lake system. Figure 7 shows the overlay of the hydrological model onto the pre-Quaternary map, and Figure 8 presents its overlay onto the Quaternary map.

Fig. 7. Integrated geological/hydrological model of Lake Turgoyak system based on the pre-Quaternary map. For lithological legend references, see Fig. 2.
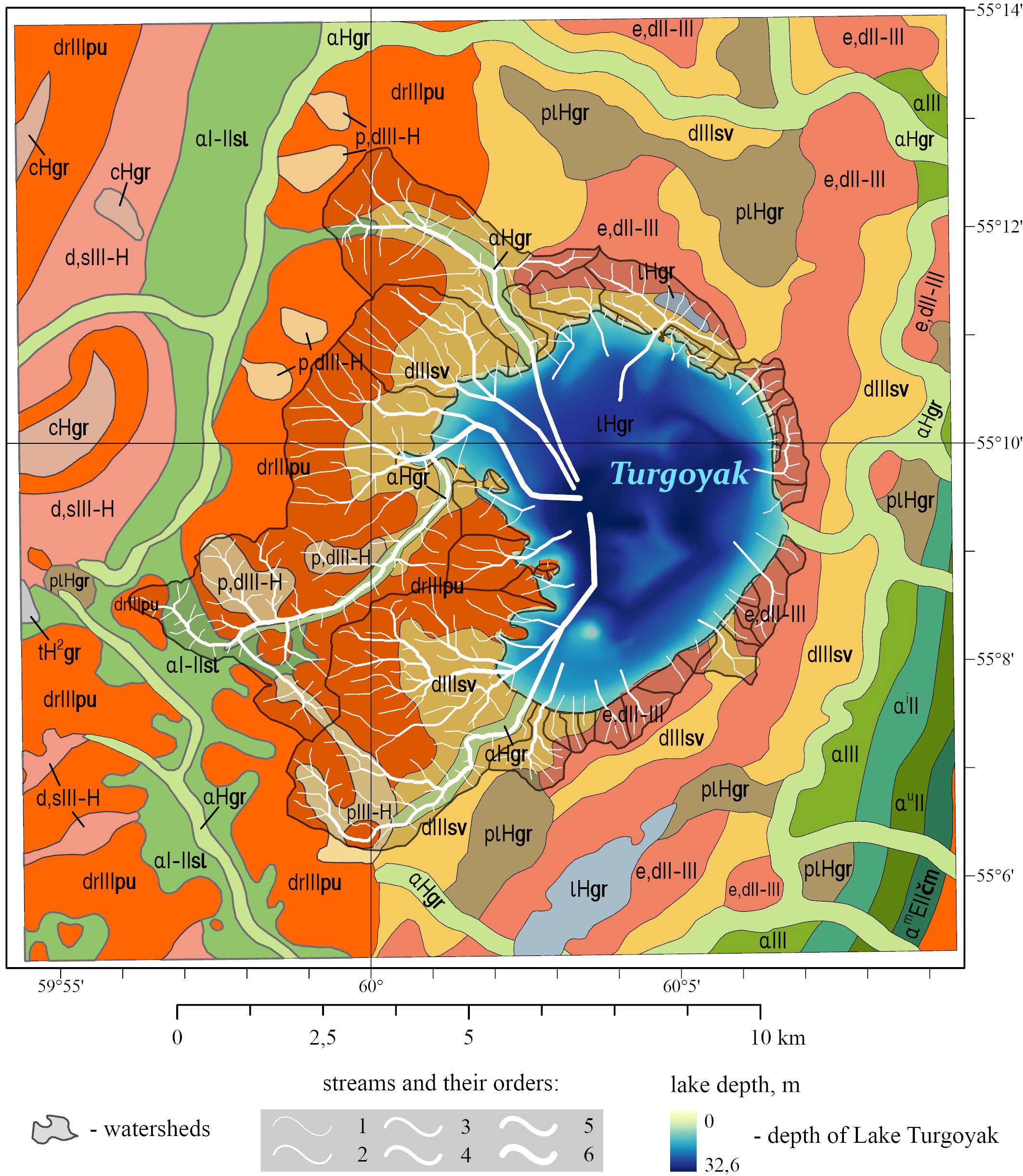
Fig. 8. Integrated geological/hydrological model of Lake Turgoyak system based on the Quaternary map. For lithological legend references, see Fig. 3.
Modeling results (Figures 5–7) showed that Lake Turgoyak’s total watershed area spans 52.5 km² and comprises 43 sub-areas. Only four of them are large ones (those of the rivers Lipovka, Mokhovaya, Bobrovka, Kuleshovka, and Pugachyovka): in total, they account for 81% of the entire watershed area, framing the lake’s northwest, west, and southwest shores.
The combined digital models of pre-Quaternary and Quaternary deposits (Figs. 2, 3, 7, 8) clearly demonstrate that the pre-Quaternary rocks are overlain by Quaternary sediments, 2–100 m thick (with a weighted average of 12 m across the watershed area). Although pre-Quaternary bedrock outcrops at the surface as weathering remnants, dikes, and intrusive contacts (Petrov et al., 2015), Quaternary deposits serve as the primary source of sedimentary material entering the lake. This is because the surface exposure area of pre-Quaternary rocks is negligible compared to the extensive coverage of Quaternary sedimentary deposits.
The largest watershed, measuring 17.4 km², belongs to the Bobrovka River basin on the western side of the lake. Quaternary deposits (Fig. 8) here are represented by a wide range of sedimentary rocks. The most extensive coverage (13.61 km²) consists of Neopleistocene deposits. Deserpation deposits of the Polyarnouralskiy Horizon (drIIIpu), reaching thickness of up to 15 m, are distributed across 9.28 km². Deluvial deposits of the Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv), up to 6 m thick, cover 2.91 km², while alluvial deposits from ancient river valleys of the Neopleistocene Sylvitskiy Horizon (αI-IIsl), with thickness of up to 31 m, occupy 1.42 km². Upper Neopleistocene-Holocene deposits cover 2.45 km² and are represented by proluvial and deluvial formations (pIII-H and p,dIII-H), with thicknesses reaching 44 m. Holocene deposits here are poorly developed (1.04 km²), consisting of alluvial floodplain and riverbed deposits (αHgr) up to 10 m thick and lacustrine deposits (lHgr) up to 2 m thick. Pre-Quaternary formations (Fig. 7) underlie 11.85 km² and are represented by rocks of the Turgoyakskiy granitoid Massif (γδС1–2ts1), while 4.43 km² features crystalline schist interlayered with carbonaceous formations and marble from the Urenginskaya Suite (RF2ur). An area of 0.76 km² is represented by two-feldspar granite with predominant plagioclase from the Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy diorite-granodiorite-granite complex (γpС1–2ts2).
The western side also includes 8 additional watershed areas totaling 2.08 km² (Fig. 8). The largest area (1.99 km²) is represented by Pleistocene deposits: 1.75 km² consist of boulders, rubble, and sandy clay with rubble from the Polyarnouralskiy Horizon (drIIIpu) up to 15 m thick, while 0.24 km² comprise brown loam with gruss, rubble, and sparse local gravel from the Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv) up to 6 m thick. Lacustrine deposits of the Holocene Gorbunovskiy Horizon (lHgr) cover 0.06 km² and consist of sand, silt, and silty clay up to 2 m thick. The pre-Quaternary formations (Fig. 7) are composed of rocks from the Turgoyakskiy granitoid Massif (γδС1–2ts1).
It should be noted that the steepest terrain slopes (up to 33°; Fig. 6) occur in areas with Polyarnouralskiy Horizon deserpation deposits overlying the Turgoyakskiy pluton rocks. Significantly gentler slopes are found in areas with Quaternary deposits (αI-IIsl, drIIIpu, p,dIII-H, αHgr) overlying crystalline schists of the Urenginskaya Suite.
The watershed of the Pugachevka and Kuleshovka rivers covers 12.88 km². It is located in the southwest and is distinguished by rocks from various stratigraphic complexes. An area of 10.21 km² is covered by Quaternary deposits (Fig. 8) represented by Pleistocene sedimentary rocks: deserpation deposits of the Polyarnouralskiy Horizon (drIIIpu) up to 15 m thick occupy 6.12 km², while deluvial deposits of the Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv) up to 6 m thick cover 4.09 km². Proluvial deposits (pIII-H) ranging from 5 to 10 m in thickness account for 1.59 km². An additional 1.10 km² consists of deposits from the Gorbunovskiy Horizon (αHgr and lHgr with thicknesses up to 2 m and 10 m respectively). An area of 6.93 km² is characterized by rocks from the Turgoyakskiy Massif (γδС1–2ts1); 4.05 km² is occupied by rocks of the Urenginskaya Suite (RF2ur); 1.23 km² is represented by basic effusives of the Polyakovskaya Suite (О1–2 pl) – sodium aphyric basalt, siliceous-clay schist, and siliceous tuffite; 0.39 km² features dunite, harzburgite, wehrlite, clinopyroxenite, and gabbro of the Sakmarskiy complex (υσО2s), and 0.28 km² encompasses quartz diorite of the first phase of the Turgoyaksko-Syrostanskiy diorite-granodiorite-granite complex (qδС1–2ts1) (Fig. 7). A narrow strip of black carbonaceous schist of the Sakmarskaya Suite (S1-D1sk) is found on the right bank of the Pugachevka River. These rocks are represented by carbonaceous-siliceous and carbonaceous-clay black schist with small phosphorite inclusions, permeated by a network of quartzite veins. It’s worth noting that towards the southwest, there’s a gradual decrease in the intensity of metamorphism, and the aphyric basalts retain their typical basaltic structure (Snachev et al. 2020). The terrain slope in the watershed area is generally 2–6°, reaching up to 20° in the southern part (Fig. 6).
The watersheds of the Mokhovaya and Lipovka rivers are located on the northwestern side. Their total areas are 3.63 km² and 6.57 km² respectively. The watershed of the Mokhovaya River is predominantly composed of deposits from the Severouralskiy Superhorizon (drIIIpu) and Polyarnouralskiy Horizon (dIIIsv) of the Pleistocene. Brown loam with gruss, rubble, and sparse local gravel (up to 6 m thick), along with boulders, rubble, and sandy clay containing rubble (up to 15 m thick), overlie crystalline schists of the Urenginskaya Suite (RF2ur, 2.56 km²) and rocks of the Turgoyakskiy Massif (γδС1–2ts1, 1.17 km²). Near the lake shores, lacustrine deposits of the Gorbunovskiy Horizon (lHgr, 0.08 km²) are present. The steepest terrain slopes (up to 33°; Fig. 6) occur in areas with Polyarnouralskiy Horizon deposits along the watershed boundaries.
The watershed of the Lipovka River (5.64 km²) is composed of Pleistocene deposits. Severouralskiy Superhorizon deposits (drIIIpu) cover 2.88 km², Polyarnouralskiy Horizon deposits (dIIIsv) occupy 2.08 km², while eluvial-deluvial formations (e,dII-III) up to 2 m thick account for 0.48 km², and alluvial deposits of ancient river valleys from the Neopleistocene Sylvinskay Horizon (αI-IIsl) up to 31 m thick make up 0.20 km². Alluvial floodplain and riverbed deposits of the Holocene Gorbunovskiy Horizon (αHgr) up to 10 m thick cover 1.06 km². Pre-Quaternary deposits occupy 2.74 km² and consist of sedimentary rocks of the Uytashskaya Suite (RF3uš), comprising micaceous quartzitic sandstone, mica-quartz schist, and phyllites with interbeds of layered sandstone containing magnetite, hematite and zircon. The Urenginskaya Suite (RF2ur) rocks are present across 2.48 km², Turgoyakskiy granitoid Massif rocks (γδС1-2ts1) cover 0.79 km², and basic effusives of the Polyakovskaya Suite (O1-2pl) extend over 0.69 km². The southern watershed features steep slopes reaching 33° (Fig. 6), where Pleistocene Polyarnouralskiy Horizon deserpation deposits overlie predominantly Urenginskaya Suite basement rocks, with minor coverage of Uytashskaya Suite deposits.
Nine watersheds with a total area of 3.90 km² are located to the north. Pleistocene rocks are distributed across an area of 3.30 km². Deluvial deposits of the Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv) cover 2.04 km², while eluvial-deluvial formations (e,dII-III) occupy 1.26 km², represented by weathered rubble of bedrock with loamy matrix, gruss, and sparse pebbles up to 2 m thick. Holocene deposits are primarily represented by lacustrine formations (lHgr) covering 0.58 km² and alluvial floodplain and channel deposits of the Gorbunovskiy Horizon (αHgr) occupying 0.02 km². Pre-Quaternary deposits across 3.17 km² consist of rocks from the Turgoyakskiy Massif (γδС1–2ts1), and the remaining portion consists of the second-phase granite (γpС1–2ts2). Along the shore, basalt has been transformed into typical hornblende plagioslate, composed of hornblende and plagioclase with finely dispersed magnetite grains (Snachev et al., 2020). The steepest terrain slopes (up to 20°; Fig. 6) occur along the northern watershed boundaries and lake shores.
The eastern side contains the largest number of watersheds. Their total area is not large, amounting to 3.21 km². The largest area of 2.46 km² is occupied by eluvial-deluvial deposits (e,dII-III) up to 2 m thick. A smaller area of 0.54 km² is covered by deluvial deposits of the Pleistocene Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv). Sand, silt, and silty clay of lacustrine deposits from the Holocene Gorbunovskiy Horizon (lHgr), up to 2 m thick, cover 0.21 km². Pre-Quaternary formations, represented by rocks of the Polyakovskaya Suite (O1–2pl), occupy the largest area of 2.12 km². The lower boundary of this stratum is tectonic and follows the Main Uralian Fault. An area of 1.00 km² is mapped with rocks of the Sakmarskiy Complex (υσO2s1), consisting of dunite, serpentinized harzburgite, talc-carbonate and talc rocks, and listvenite, while 0.09 km² contains rocks of the Turgoyakskiy Massif (γδC1-2ts1). In the contact zone with the Turgoyakskiy Massif, the rocks of the Polyakovskaya Suite are intensely amphibolized. Along the lake shoreline within the area of Polyakovskaya Suite rocks, the steepest terrain slopes are observed, reaching 33° (Fig. 6).
To the south, the lake is bordered by 7 watersheds with a total area of 2.50 km². The majority of the area (2.41 km²) is covered by eluvial-deluvial deposits (e,dII-III, 1.51 km²) up to 2 m thick and deluvial deposits of the Pleistocene Severouralskiy Superhorizon (dIIIsv, 0.90 km²). Palustrine deposits (plHgr), consisting of silty clay, peaty clay, and peat up to 8 m thick, occupy 0.09 km². Pre-Quaternary formations across 2.20 km² comprise basic effusives of the Polyakovskaya Suite (O1-2pl), while 0.30 km² consists of rocks from the Turgoyakskiy Massif (γδC1-2ts). The steepest slopes (Fig. 6) are observed along the lake shoreline.
The newly developed digital model highlights the lake’s pelagic zone, defined by western and eastern depressions. The pelagic zone borders the littoral zone, which is least developed in the eastern part of the lake. The maximum depth of the lake in the model reaches 32.6 m, which is consistent with published data (Zakharov, 2020; Andreeva, 1973).
In the eastern slopes of the Southern Urals, lacustrine sediments typically accumulate primarily in the pelagic zone, either on the surface of weathered clay crusts or dense Neogene clays (Petrov et al., 2015). This depositional pattern likely applies to the studied lacustrine sediments as well (Kosareva et al., 2023). Given that the lake has throughflow, sediment movement in the lake system includes its input, output, and transport within the lake, which is driven by processes such as sedimentation itself, diffusion due to concentration gradients, exchange between deep and surface waters, bacterial decomposition of organic particles, primary bioproduction, and transfer of matter from the lake biosphere to the geosphere (Hakanson, 2012).
The composition of lake sediments is defined by both allochthonous material and water components, which include dissolved gases, dissolved solids, suspended solids, and suspended organisms. Studies of sediment cores from Lake Turgoyak confirm their complex material composition (Maslennikova et al., 2018; Kosareva et al., 2023).
Whenever currents occur in the upper water layers, an exchange of components takes place between the littoral and pelagic zones. Chemical differences between the top few meters of the pelagic and littoral zones may arise due to biological processes, but only under low current conditions.
Lake sediments form through the deposition of organic matter and minerals from the lake’s drainage divides, as well as organic matter consisting of fecal pellets, organic debris (detritus), and skeletal fragments of organisms originating from the lake itself. Continuous deposition of this fine mixed solid material occurs throughout the entire lake. Disturbance of sediments by moving water primarily occurs in shallow areas, where most of the energy from wind-driven currents and waves is expended on the littoral bottom. Therefore, movements in near-shore areas can cause fine-grained sediments to be transported into deeper zones. For this reason, lacustrine sediments may not accumulate uniformly throughout the littoral zone (Lewis, 2009), a pattern that seismic and acoustic data (Kosareva et al., 2023) confirms is also characteristic of Lake Turgoyak.
Seismic data from a profile running across Lake Turgoyak southwest to east reveal that the southwestern slope of the lake basin is more gradual, while the northeastern slope is steep (Kosareva et al., 2023). Sediment distribution within the basin is uneven, with deposition occurring mainly in the pelagic zone. Notably, the thickest sediment layer, measuring 8 m, is located in the eastern part of the lake. Sedimentation rate varies across the basin, with the deeper northeastern section accumulating sediments more rapidly (Deryagin, 2018). The average sedimentation rate over the past century has been 1.75 mm/year (Zakharov, 2020).
The composition of allochthonous material accumulating on the lake’s drainage divides is determined by the composition of rocks surrounding the lake, including those in erosion areas and along sediment transportation pathways.
The western shoreline of the lake is composed primarily of Neopleistocene slope deposits, specifically boulders, rubble and clay, with lesser amounts of loam, rubble, clay and sand of deluvial and alluvial origin. Loam dominates in proluvial and deluvial deposits of the Upper Neopleistocene-Holocene, while sand prevails in alluvial floodplain and riverbed deposits and Holocene lacustrine formations.
The southwestern shoreline is characterized by the distribution of boulders, rubble and clay from deserpation deposits, loam and rubble from Pleistocene deluvial formations, as well as loam and sand from Upper Neopleistocene-Holocene proluvial deposits. Holocene deposits here are represented mainly by sand.
The northwestern areas adjacent to the lake show predominance of loam, rubble, bouldery and clayey materials of Neopleistocene age, and sand from Holocene lacustrine and alluvial deposits.
Numerous northern and eastern drainage basins are composed primarily of boulders and rubble, with lesser amounts of clayey material. The Holocene is represented mainly by sand from lacustrine deposits and alluvial floodplain and riverbed deposits.
The southern watershed areas consist of Pleistocene eluvial-deluvial and deluvial formations, predominantly rubble and boulders. Holocene palustrine deposits are composed of silty clay and peat.
It is evident that all described areas supply the lake with allochthonous sedimentary material formed through processes of physical, chemical and biological weathering of continental facies deposits (eluvium, deluvium, proluvium, alluvium) and typically containing mature mineral components (quartz, feldspars, talc, hornblende, zircon, etc.).
It should be noted that the digital model of the Turgoyak lake system developed in this study meets modern standards for such models. The accuracy of the DEM (30 m resolution) is ensured by Copernicus DEM GLO-30 satellite data (European Space Agency), which is comparable in accuracy to Landsat 7 and 8 data (NASA) commonly used for similar studies. However, it should be noted that both Copernicus DEM GLO-30 and Landsat 7/8 data are less accurate than data from satellites specifically designed for detailed Earth surface studies, such as the Sentinel-2 mission satellites in polar orbit that provide imagery with up to 10 m resolution.
The digital model presented in this study offers significant advantages over its analogs (Masoud et al., 2021; Rongali et al., 2024; Potakhin et al., 2024) by including not just the DEM but also lake bathymetry, drainage divides, watershed boundaries, surface slopes, and drainage networks. The watersheds are represented by outcropping Quaternary deposits and pre-Quaternary formations.
There are clear prospects for further developing and enhancing the model. International practice demonstrates the value of long-term monitoring approaches, which could also be applied to studies of Lake Turgoyak. Future improvements could incorporate more detailed geological maps and higher-resolution bathymetric data. Additional potential exists for quantifying sediment inputs to the lake if hydrological monitoring data becomes available for inflowing rivers, particularly measurements of average annual water discharge and sediment loads.
This model will serve as a foundation for various future studies of Lake Turgoyak, including investigation of bottom sediment characteristics in relation to lake morphometry, sediment sources, and other factors and processes of lacustrine sedimentogenesis, as well as enabling reconstructions of the lake’s evolution and tracking changes in its morphometric characteristics during different climatic periods of the past.
Conclusion
For the first time, a digital model has been created in a GIS environment for Lake Turgoyak, showcasing its geological, topographic, and hydrological characteristics along with its surrounding areas. The created digital model holds significant importance for advancing our understanding of the structure and genesis of lacustrine and other associated facies in the Southern Urals. The creation of similar digital models for lake systems in the Urals, other regions of Russia. and the world opens new possibilities for systematizing information at an advanced level and utilizing it for various reconstructive purposes.
Funding/Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a subsidy allocated to Kazan Federal University for the implementation of a state assignment (Project No. FZSM-2023-0023) in the field of scientific activity.
References
1. Andreeva M.A. (1973). Lakes of the Middle and Southern Urals. Chelyabinsk: Yuzh.-Ural. Publ. (In Russ.)
2. Artaev O.N., Bayanov N.G. (2015). Morfometriya Muhtolovskih ozyor. Opyt postroeniya modelej ozyornyh kotlovin v GIS. Trudy Mordovskogo gosudarstvennogo prirodnogo zapovednika im. P.G. Smidovicha, (14), pp. 199–211. (In Russ.)
3. Astashin A.E., Badin M.M., Kartashov A.Yu., Goryachev A.S., Voznesenskaya M.V., Karabanov A.D., Pashkin M.N. (2016). Morphometric Characteristics of The Lakes Parovoe, Kruglenkoe, Glubokoe Of The State Natural Biological Wildlife Area “Pustynsky” (Nizhny Novgorod Region). International Research Journal, 8(50), pp. 49–54. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.18454/IRJ.2016.50.177
4. Aulov B.N., Vladimirceva Yu.A., Gvozdik N.I., Korolkova Z. G., Levin F. D., Lipaeva A. V., Potashova M. N., Samozvantsev V. A. (2015). State Geological Map of the Russian Federation. Scale 1:200,000. Second edition. South Ural series. Sheet N-40-XII – Chrysostom. Explanatory note. Moscow: VSEGEI, 365 p. (In Russ.)
5. Gavrilkina S.V., Korableva O.E., Mityuhlyaev D.V., Rogozin A.G., Tanaeva G.V., Tkachev V.A., Shimanskij L.I. (1998). Ecology of Lake Turgoyak. Miass: Institute of Geographical Zoology Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. (In Russ.)
6. Grigoriev S., Vasina Yu. (2019). The Megaliths of Vera Island in the Southern Urals. Archaeopress. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvndv6hm
7. Grigoriev S. A., Vasina Yu. V. (2020). Megalithic complex and settlements of the Island of Vera. Chelyabinsk: Abris, 307 p. (In Russ.)
8. Deryagin V.V. (2018). Stratification of bottom sediments near the northern and southern shores of Lake Turgoyak (Southern Urals). Proc. Conf.: Problems of the geography of the Urals and adjacent territories. Chelyabinsk: Krai Ra, pp. 94–100. (In Russ.)
9. Diyanova O.P., Deryagin V.V. (2010). Lithologic-geomorphological characteristics of some lakes of South Urals and the Trans-Ural. Bulletin of the Moscow Region State University. Series Natural Sciences, (2), pp. 106–112. (In Russ.)
10. ESRI ArcGIS Pro (2024). An overview of the Spatial Analyst. https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/3.0/tool-reference/spatial-analyst/an-overviewof-the-spatial-analyst-toolbox.htm
11. Hakanson L. (2012). Sedimentation Processes in Lakes. In: Bengtsson L, Herschy RW, Fairbridge RW (eds) Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4410-6_3
12. Kosareva L.R., Nurgalieva N.G., Nurgaliev D.K., Li H, Krylov P.S., Kuzina D.M., Antonenko V.V. (2023). Preliminary Magnetic Mineralogical Studies of the Neopleistocene-Holocene Sediments from Lake Turgoyak. Uchenye Zapiski Kazanskogo Universiteta. Seriya Estestvennye Nauki, 165(4), pp. 563-576. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.26907/2542-064X.2023.4.563-576
13. Kostryukova A., Mashkova I., Belov S., Shchelkanova E., Trofimenko V., Kargina V. (2022). Assessing relationship of degradation of coastal zones and phytoplankton species structure of Lake Uvildy and Lake Turgoyak (South ural, russia) IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/958/1/012002
14. Lewis W.M. (2009). Ecological zonation in lakes – Encyclopedia of Inland Waters. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012370626-3.00209-X
15. Maslennikova A.V., Udachin V.N., Deryagin V.V., Shtenberg M.V. (2018). Reconstruction of Turgoyak lake (the Southern Urals) ecosystem changes in Holocene. Lithosphere (Russia), 18(6), pp. 914–927. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.24930/1681-9004-2018-18-6-914-927
16. Masoud A.A., El-Horiny M.M., Khairy H.M., El-Sheekh M.M. (2021). Phytoplankton dynamics and renewable energy potential inducedby the environmental conditions of Lake Burullus, Egypt. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15625-4
17. Menberu Z., Mogesse B., Reddythota D. (2021). Assessment of morphometric changes in Lake Hawassa by using surface and bathymetric maps. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100852 Mishutkina M.Yu., Kagarmanova M.U., Rozhnova E.S. (2021).
18. Expedition “Turgoyak-2021”. Proc. II International Scientific and Practical Conference: Geographical space: balanced development of nature and society. Chelyabinsk, pp. 110–114. (In Russ.)
19. Petrov V.I, Shalaginov A.E., Punegov B.N. Gorlova L. I., Zabelkina L. G., Grigorova T. B., Nikolsky V. Yu., Shalaginova T. I., Petrova A. S., Sereda V. V. (2015). State Geological Map of the Russian Federation. Scale 1:200 000. Second Edition. South Ural Series. Sheet N-41-VII. Explanatory Note. Moscow: VSEGEI, 168 р. (In Russ.)
20. Qin Y., Zhang Ch., Lu P. (2023). A fully automatic framework for subpixel mapping of thermokarst lakes using Sentinel-2 images. Science of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.srs.2023.100111
21. Rogozin A.G., Takachev V.A. (1998). On some hydrological features of Lake Turgoyak. Izvestiya Chelyabinskogo Nauchnogo Tsentra, (1), pp. 70–75, (In Russ)
22. Rongali G., Tiwari K.C., Vishwas P. (2024). Mapping of Glacial Lakes and Glacial Lake Outburst Flood in Lahul and Spiti District Using Remote Sensing and GIS. In: Biswas B, Ghute BB (eds) Flood Risk Management. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2688-2_3
23. Snachev A.V., Snachev V.I., Romanovskaya M.A. (2020). Geology, formation conditions, and ore content of the Turgoyak granite massif and carbonaceous deposits of its western framing (South Ural). Moscow University Bulletin. Series 4. Geology, (1), pp. 12–20. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.33623/0579-9406-2020-1-12-20
24. Special Protection Natural Areas of Russia (2024). Lake Turgoyak. (In Russ.) https://oopt.gov74.ru/oopt/overview/oopt/ozeroturgoyak.htm
25. Tarboton DG, Bras RL, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (1991). On the Extraction of Channel Networks from Digital Elevation Data. Hydrological Processes, 5, pp. 81–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050107
26. The European space agency (2024). DEM – Global and European Digital Elevation Model (COP-DEM). https://spacedata.copernicus.eu/collections/copernicus-digital-elevation-model
27. Turgoyak. The lake is a natural monument and its surroundings (1993). Ed. Terentyev M.M., Moiseev A.P. Chelyabinsk: Rifey. (In Russ.)
28. Fershtater G.B., Shagalov E.S., Bea F., Montero P. (2000). TurgoyakSyrostan group of granitoid massifs of the Main Ural deep fault zone. Magmatic and metamorphic formations of the Urals and their metallogeny. Ekaterinburg: IGiG UB RAS, pp. 129–158. (In Russ.)
29. Shagalov E.S. (1999). On the petrography and geochemistry of rocks of the Turgoyak massif (Southern Urals). Yearbook-1999. Ekaterinburg: IGiG UrO RAN, pp. 129–156 (In Russ.)
30. Zakharov S.G. (2018). Lake Turgoyak — the adornment of the Ural land. Uralskiy sledopyt, (11), pp. 16–23. (In Russ.)
31. Zakharov S.G. (2020). Dynamics of environmental status of the lake Turgoyak. Proceedings of the Russian Geographical Society, 152(1), pp. 56–65. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869607120010085
32. Zakharov S.G. (2021). Anthropogenic eutrophication of lakes Turgoyak and Bolshoi Kisegach. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/834/1/012048
About the Authors
I. Yu. ChernovaRussian Federation
Inna Yu. Chernova – Cand. Sci. (Geology and Mineralogy), Associate Professor of the Department of Geophysics and Geoinformation Technologies
4/5, Kremlevskaya str., Kazan, 420008
L. R. Kosareva
Russian Federation
Lina R. Kosareva – Cand. Sci. (Geology and Mineralogy), Senior Researcher, Scientific and Research Center “Digital Earth”
4/5, Kremlevskaya str., Kazan, 420008
N. G. Nourgalieva
Russian Federation
Nouria G. Nourgalieva – Dr. Sci. (Geology and Mineralogy), Professor, Department of Oil and Gas Geology, Institute of Geology and Petroleum Technology
4/5, Kremlevskaya str., Kazan, 420008
O. S. Chernova
Russian Federation
Olga S. Chernova – Junior Researcher, World-Class Scientific Center Rational Development of Liquid Hydrocarbon Reserves of the Planet, Research Laboratory for the Study of Oil and Gas Accumulation Basins
4/5, Kremlevskaya str., Kazan, 420008
Supplementary files
|
|
1. Three-dimensional visualization of the DEM | |
| Subject | ||
| Type | Результаты исследования | |
View
(118MB)
|
Indexing metadata ▾ | |
|
|
2. A 3D local scene sequentially displaying the DEM, hillshade, and slope | |
| Subject | ||
| Type | Результаты исследования | |
View
(81MB)
|
Indexing metadata ▾ | |
|
|
3. The DEM is overlayed by the geological map of pre-Quaternary formations | |
| Subject | ||
| Type | Результаты исследования | |
View
(199MB)
|
Indexing metadata ▾ | |
|
|
4. The DEM is overlayed by the geological map of Quaternary deposits | |
| Subject | ||
| Type | Результаты исследования | |
View
(102MB)
|
Indexing metadata ▾ | |
Review
For citations:
Chernova I.Yu., Kosareva L.R., Nourgalieva N.G., Chernova O.S. Digital Model of the Turgoyak Lake System, Southern Urals. Georesursy = Georesources. 2025;27(2):264–280. https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2025.2.20















.png)


